结合Python的SimpleHTTPServer源码来解析socket通信
何谓socket
计算机,顾名思义即是用来做计算。因而也需要输入和输出,输入需要计算的条件,输出计算结果。这些输入输出可以抽象为I/O(input output)。
Unix的计算机处理IO是通过文件的抽象。计算机不同的进程之间也有输入输出,也就是通信。因此这这个通信也是通过文件的抽象文件描述符来进行。
在同一台计算机,进程之间可以这样通信,如果是不同的计算机呢?网络上不同的计算机,也可以通信,那么就得使用网络套接字(socket)。socket就是在不同计算机之间进行通信的一个抽象。他工作于TCP/IP协议中应用层和传输层之间的一个抽象。如下图:
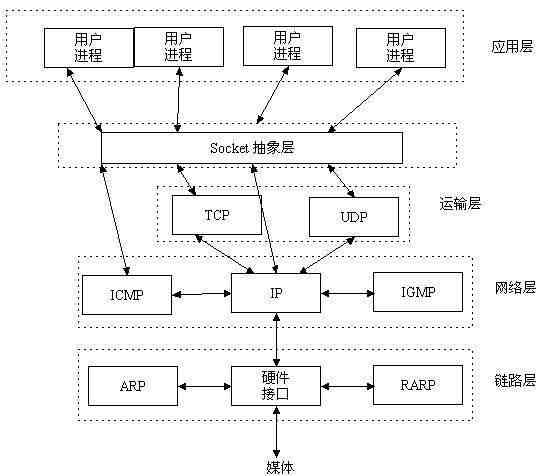
服务器通信
socket保证了不同计算机之间的通信,也就是网络通信。对于网站,通信模型是客户端服务器之间的通信。两个端都建立一个socket对象,然后通过socket对象对数据进行传输。通常服务器处于一个无线循环,等待客户端连接:
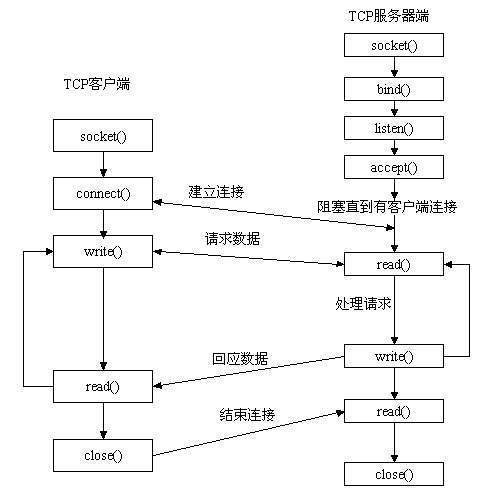
socket 通信实例
socket接口是操作系统提供的,调用操作系统的接口。当然高级语言一般也封装了好用的函数接口,下面用python代码写一个简单的socket服务端例子:
server.py
import socket
HOST = \'localhost\' # 服务器主机地址
PORT = 5000 # 服务器监听端口
BUFFER_SIZE = 2048 # 读取数据大小
# 创建一个套接字
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# 绑定主机和端口
sock.bind((HOST, PORT))
# 开启socket监听
sock.listen(5)
print \'Server start, listening {}\'.format(PORT)
while True:
# 建立连接,连接为建立的时候阻塞
conn, addr = sock.accept()
while True:
# 读取数据,数据还没到来阻塞
data = conn.recv(BUFFER_SIZE)
if len(data):
print \'Server Recv Data: {}\'.format(data)
conn.send(data)
print \'Server Send Data: {}\'.format(data)
else:
print \'Server Recv Over\'
break
conn.close()
sock.close()
client.py
import socket
HOST = \'localhost\'
PORT = 5000
BUFFER_SIZE = 1024
# 创建客户端套接字
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# 连接到服务器
sock.connect((HOST, PORT))
try:
message = \"Hello\"
# 发起数据给服务器
sock.sendall(message)
amount_received = 0
amount_expected = len(message)
while amount_received < amount_expected:
# 接收服务器返回的数据
data = sock.recv(10)
amount_received += len(data)
print \'Client Received: {}\'.format(data)
except socket.errno, e:
print \'Socket error: {}\'.format(e)
except Exception, e:
print \'Other exception: %s\'.format(e)
finally:
print \'Closing connection to the server\'
sock.close()
TCP 三次握手
python代码写套接字很简单。传说的TCP三次握手又是如何体现的呢?什么是三次握手呢?
第一握:首先客户端发送一个syn,请求连接,
第二握:服务器收到之后确认,并发送一个 syn ack应答
第三握:客户端接收到服务器发来的应答之后再给服务器发送建立连接的确定。
用下面的比喻就是
C:约么?
S:约
C:好的
约会
这样就建立了一个TCP连接会话。如果是要断开连接,大致过程是:
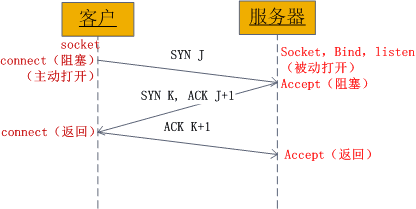
上图也很清晰的表明了三次握手的socket具体过程。
- 客户端socket对象connect调用之后进行阻塞,此过程发送了一个syn。
- 服务器socket对象调用accept函数之后阻塞,直到客户端发送来的syn,然后发送syn和ack应答
- 客户端socket对象收到服务端发送的应答之后,再发送一个ack给服务器,并返回connect调用,建立连接。
- 服务器socket对象接受客户端最后一次握手确定ack返回accept函数,建立连接。
至此,客户端和服务器的socket通信连接建立完成,剩下的就是两个端的连接对象收发数据,从而完成网络通信。
SimpleHTTPServer
构建一个简单的HTTP服务,需要继承HTTPServer,同时requesthandler也需要继承BaseHTTPRequestHandler。python已经实现了一个例子,那就是SimpleHTTPServer。因此分析SimpleHTTPServer来查看如何使用前面的一些类构建http服务。
曾经为了表示python的简洁优雅,经常会举这样的例子,python可以一行代码开启一个服务器。
$ python -m SimpleHTTPServer
这里的SimpleHTTPServer就是实现了HTTPServer的模块。
SimpleHTTPServer通过调用BaseHTTPServer模块的test方法做为入口。
def test(HandlerClass = SimpleHTTPRequestHandler,
ServerClass = BaseHTTPServer.HTTPServer):
BaseHTTPServer.test(HandlerClass, ServerClass)
test方法做了两件事,第一件就是使用HTTPServer接受一个监听地址和requestClass参数,创建了一个实例对象,调用server_forever方法开启服务。
1.SimpleHTTPRequestHandler
根据之前的分析,使用httpserver的服务,我们只需要继续BaseHTTPRequestHandler,并提供自省的method方法即可。
class SimpleHTTPRequestHandler(BaseHTTPServer.BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
server_version = \"SimpleHTTP/\" + __version__
def do_GET(self):
f = self.send_head()
if f:
self.copyfile(f, self.wfile)
f.close()
def do_HEAD(self):
f = self.send_head()
if f:
f.close()
do_GET 和 do_HEAD 分别实现了http的get请求和head请求的处理。他们调用send_head方法:
def send_head(self):
path = self.translate_path(self.path)
f = None
if os.path.isdir(path):
if not self.path.endswith(\'/\'):
self.send_response(301)
self.send_header(\"Location\", self.path + \"/\")
self.end_headers()
return None
for index in \"index.html\", \"index.htm\":
index = os.path.join(path, index)
if os.path.exists(index):
path = index
break
else:
return self.list_directory(path)
ctype = self.guess_type(path)
try:
f = open(path, \'rb\')
except IOError:
self.send_error(404, \"File not found\")
return None
self.send_response(200)
self.send_header(\"Content-type\", ctype)
fs = os.fstat(f.fileno())
self.send_header(\"Content-Length\", str(fs[6]))
self.send_header(\"Last-Modified\", self.date_time_string(fs.st_mtime))
self.end_headers()
return f
send_head 方法通过uri的path分析得到客户请求的网路路径。构造head的mime元信息并发送到客户端,然后返回一个打开path的文件句柄。
2.copyfile
do_GET的下一步就是通过 copyfile方法,将客户请求的path的文件数据写入到缓冲可写文件中,发送给客户端。
3.list_directory
SimpleHTTPServer模块还提供了list_directory方法,用于响应path是一个目录,而不是文件的情况。
def list_directory(self, path):
try:
list = os.listdir(path)
except os.error:
self.send_error(404, \"No permission to list directory\")
return None
list.sort(key=lambda a: a.lower())
f = StringIO()
displaypath = cgi.escape(urllib.unquote(self.path))
f.write(\'\')
f.write(\"\\nDirectory listing for %s \\n\" % displaypath)
f.write(\"\\nDirectory listing for %s
\\n\" % displaypath)
f.write(\"
\\n- \\n\")
for name in list:
fullname = os.path.join(path, name)
displayname = linkname = name
# Append / for directories or @ for symbolic links
if os.path.isdir(fullname):
displayname = name + \"/\"
linkname = name + \"/\"
if os.path.islink(fullname):
displayname = name + \"@\"
# Note: a link to a directory displays with @ and links with /
f.write(\'
- %s\\n\' % (urllib.quote(linkname), cgi.escape(displayname))) f.write(\"
\\n\\n\\n\") length = f.tell() f.seek(0) self.send_response(200) encoding = sys.getfilesystemencoding() self.send_header(\"Content-type\", \"text/html; charset=%s\" % encoding) self.send_header(\"Content-Length\", str(length)) self.end_headers() return f
由此可见,处理客户端的请求,只需要使用 send_reponse, send_header 和 end_headers ,就能向客户端发送reponse。
4.自定义http服务
定义一个CustomHTTPRequestHadnler继承自BaseHTTPRequestHandler。在其内实现do_GET 方法来处理get请求。
然后再定义一个CustomHTTPServer继承自HTTPServer,它接受CustomHTTPRequestHadnler作为自己的handler。简单的代码如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from BaseHTTPServer import BaseHTTPRequestHandler, HTTPServer
class CustomHTTPRequestHandler(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
def do_GET(self):
self.send_response(200)
self.send_header(\'Content-type\', \'text/html\')
self.end_headers()
self.wfile.write(\"hello world\\r\\n\")
class CustomHTTPServer(HTTPServer):
def __init__(self, host, port):
HTTPServer.__init__(self, (host, port), CustomHTTPRequestHandler)
def main():
server = CustomHTTPServer(\'127.0.0.1\', 8000)
server.serve_forever()
if __name__ == \'__main__\':
main()
使用curl访问可以得到
➜ ~ curl http://127.0.0.1:8000 hello world ➜ ~
控制台会打出访问的log。
127.0.0.1 - - [01/Jun/2015 11:42:33] \"GET / HTTP/1.1\" 200 -
从socket的建立,select的IO模式,再到Server和Handler的组合构建服务。我们已经熟悉了python的基本网络编程。python的web开发中,更多是使用WSGI协议。实现该协议的还有 uWSGI和gunicorn等库。相比那些库,python内部提供了一个wsgiref模块,实现了一个简单wsgi服务–simple_server。
接下来将会通过分析simple_server,更好的掌握WSGI协议。
