5.Python3爬虫入门实践——爬取名著
admin
2023-07-30 21:02:40
0次
1.准备工作
- 书写爬虫之前的步骤:
1.从哪爬 where
2.爬什么 what
3.怎么爬 how
4.爬了之后信息如何保存 save
我称之为WWHS,这就是最基本的步骤了。
1.1 从哪爬where和爬什么what
-
其实where和what是交融的一体,当你找到what的时候,自然就找到了where。当你确定了where时,what自然而然就知道了。
这次我们爬取诗词名句网 \”http://www.shicimingju.com/\” 的名著,如爬取“三国演义”、“隋唐演义”等。 -
爬取内容如下:
- 主页面 :[小说名字,每章的名字,每章的链接]
- 若干次页面:[每章的内容]
1.2 怎么爬How
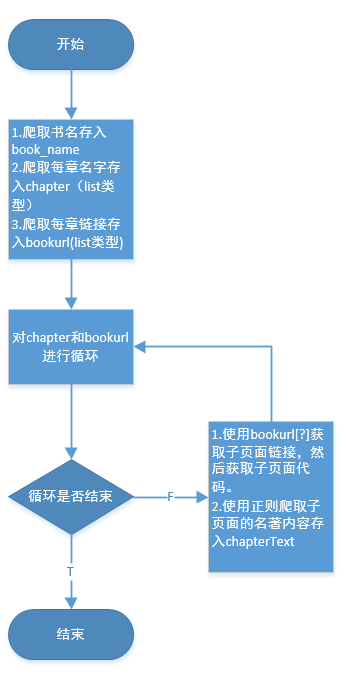
1.在主页面利用正则爬取小说名字存入book_name,然后再爬取每章的名字存入chapter,爬取每章的链接存入bookurl。
2.使用for循环一一使用bookurl[?]来爬取子页面代码。
3.利用正则将子页面代码中的每章的内容爬出来。
A picture is worth a thousand words
1.3 爬了之后信息如何保存
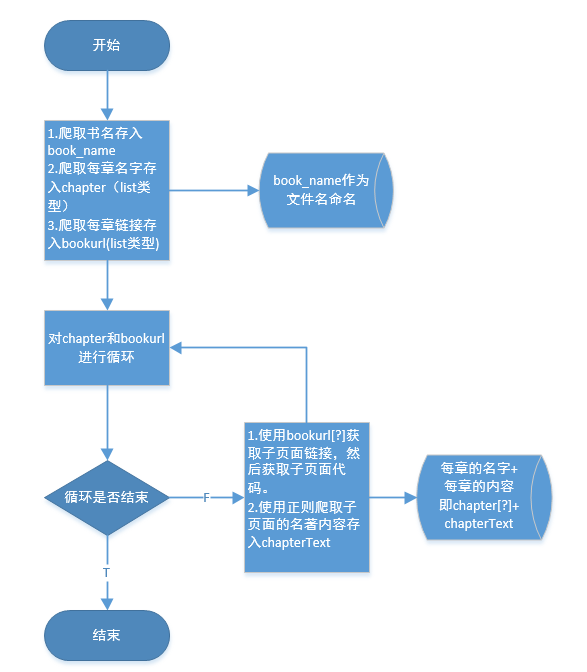
1.小说类型适合使用文件保存,不适合数据库存储。
2.将book_name作为文件名创建,利用for循环读取每章的名字chapter[?]和每章的内容chapterText存入文件,形成一个完整的小说文件。
A picture is worth a thousand words
2.编写代码
- 读取网页代码
import urllib.request import re indexUrl=\"http://www.shicimingju.com/book/sanguoyanyi.html\" html =urllib.request.urlopen(indexUrl).read() html=html.decode(\'utf8\') - 爬取书名book_name,爬取每章的名字chapter,爬取书的链接bookurl
(具体问题具体分析,我这里在爬取每章的链接的时候发现竟然是相对路径,无法直接使用,于是只能针对书的链接进行字符串修改,从而来跳转到每章的页面。)book_name=re.findall(\'(.*)
\',html,re.S) chapter=re.findall(\'href=\"/book/.{0,30}\\d\\.html\">(.*?)\',html,re.S) bookurl=re.findall(\'href=\"(/book/.{0,30}\\d\\.html)\">\',html,re.S) chapterUrlBegin=re.sub(\'.html\',\'\',indexUrl)#将书的链接替换成每章的链接开头 - 爬取每章的内容chapterText,并且输出成文件。
其中要注意看具体的输出,替换其中的一些字符和标签。for i in range(0,len(bookurl)): #提取每章的number number=re.findall(\'/(.{1,4})\\.html\',bookurl[i]) #合并字符串形成每章的链接 chapterUrl=re.sub(\'$\',\"/\"+number[0]+\".html\",chapterUrlBegin) #打开链接网页 chapterHtml=urllib.request.urlopen(chapterUrl).read() chapterHtml=chapterHtml.decode(\'utf-8\',\'ignore\') #找到每章内容 chapterText=re.findall(\'(.*?)\',chapterHtml,re.S) #替换其中的标签和 chapterText=re.sub(\'\',\'\',\'\'.join(chapterText)) chapterText = re.sub(\'
\', \'\', \'\'.join(chapterText)) chapterText = re.sub(\'\', \' \', \'\'.join(chapterText)) #输出文件 f=open(\'D://book/\'+\"\".join(book_name)+\'.txt\',\'a\',encoding=\'utf-8\') f.write(chapter[i]+\"\\n\") f.write(chapterText+\"\\n\") f.close()
3.总结
- 总的过程就一句话:
书写正则抓取网页信息,存入数据库或文件。
相关内容
热门资讯
500 行 Python 代码...
语法分析器描述了一个句子的语法结构,用来帮助其他的应用进行推理。自然语言引入了很多意外的歧义,以我们...
定时清理删除C:\Progra...
C:\Program Files (x86)下面很多scoped_dir开头的文件夹 写个批处理 定...
65536是2的几次方 计算2...
65536是2的16次方:65536=2⁶
65536是256的2次方:65536=256
6553...
Mobi、epub格式电子书如...
在wps里全局设置里有一个文件关联,打开,勾选电子书文件选项就可以了。
scoped_dir32_70...
一台虚拟机C盘总是莫名奇妙的空间用完,导致很多软件没法再运行。经过仔细检查发现是C:\Program...
pycparser 是一个用...
`pycparser` 是一个用 Python 编写的 C 语言解析器。它可以用来解析 C 代码并构...
小程序支付时提示:appid和...
[Q]小程序支付时提示:appid和mch_id不匹配
[A]小程序和微信支付没有进行关联,访问“小...
微信小程序使用slider实现...
众所周知哈,微信小程序里面的音频播放是没有进度条的,但最近有个项目呢,客户要求音频要有进度条控制,所...
python绘图库Matplo...
本文简单介绍了Python绘图库Matplotlib的安装,简介如下:
matplotlib是pyt...
Prometheus+Graf...
一,Prometheus概述
1,什么是Prometheus?Prometheus是最初在Sound...
